Tongue coating microbiome as a potential biomarker for gastritis including precancerous cascade.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/m/pubmed/30478535/?i=1&from=tongue%20diagnosis%20tcm

Achilles Shang Point Dr Mia LAc MSc
Achilles Shang Point – I named it temporary is a pressure point I’ve been using for years and receiving really well healing outcomes. It’s on the Achilles Tendon, 4 cuns above Medial Malleolus. When we palpate along the Achilles Tendon upward with dorsiflexion, you might easily find an obvious depression and that’s the point we wanna stimulate. I’ve been using it to treat all types of low back and hips pain, sore legs, ankles sprain, plantar fasciitis and any other lower extremities conditions. It seems working really well.
8DD780F4-10A8-4466-9CF1-DEE3720ABB99
On the Anatomy perspective, punctuating this point may penetrate Achilles Tendon, Soleus, Flexor hallucis longus, Flexor digitorum longus, and Tibialis posterior. Therefore, using this point to treat the associate conditions is understandable.
0117B499-953F-4324-9E85-A069923DD1A7
Based on TCM Meridian Theory, it is on the TaiYang aspect. Therefore, I assumed that it should also have the function to treat the TaiYang syndromes and diseases and TaiYang Meridians related illnesses. We are busy collecting more data on the actual clinical experiments to support my hypothetical theory on more functions and indications.
UB 55 in treating hip joint pain
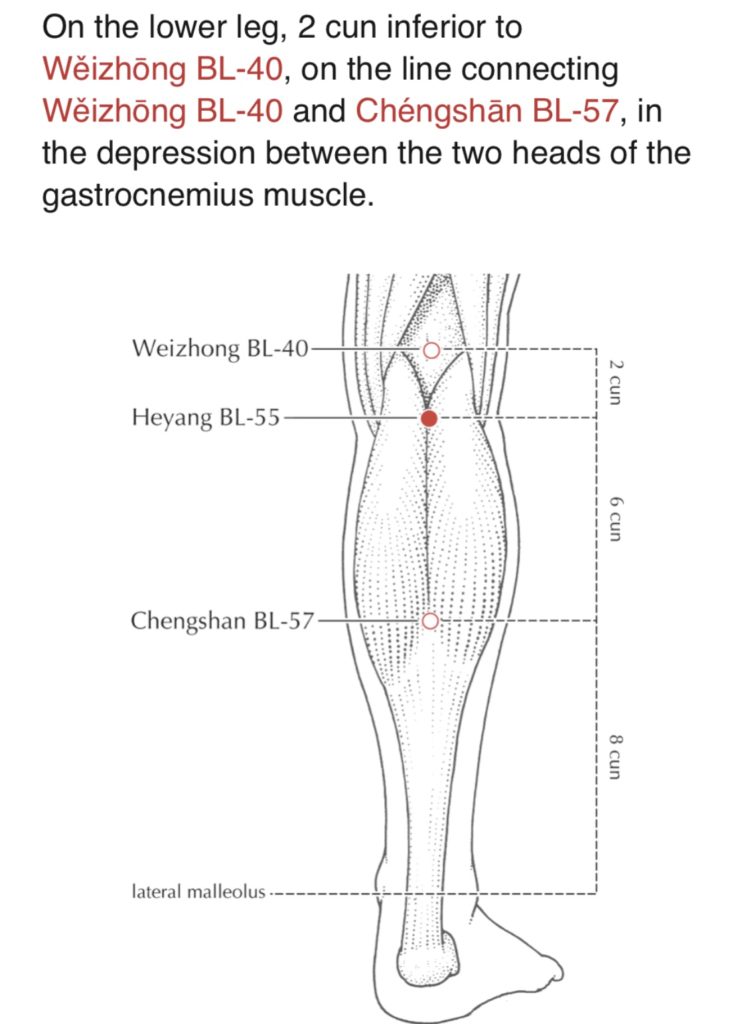 Experience sharing: I’ve been using UB 55 to treat 67 cases of hip joint pain. Cases included acute and chronic (the most was 38 years), severity from 6/10 to 10/10, limited ROM and difficulty of weight bearing.
Experience sharing: I’ve been using UB 55 to treat 67 cases of hip joint pain. Cases included acute and chronic (the most was 38 years), severity from 6/10 to 10/10, limited ROM and difficulty of weight bearing.
The results of treatment were amazingly well. All 67 patients were truly grateful for the improvements of pain and mobility. UB 55 for hip joint is worked the best while applying initiative exercise of movement and weight bearing while the needle inserting in the point with stimulating on the opposite UB55 for 5 minutes.
Traditional Chinese Medicine for Geriatric Diseases
Acupuncture and other adjunctive treatment methods have been vastly used worldwide for improvement in Quality of Life due to geriatric diseases in the elderly.
The following researches have demonstrated the effectiveness of TCM in the management of some geriatric diseases.
Effect of Acupuncture in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer Disease: A Functional MRI Study
Zhiqun Wang, 1 Binbin Nie, 2 Donghong Li, 3 Zhilian Zhao, 1 Ying Han, 4 Haiqing Song, 4 Jianyang Xu, 3 Baoci Shan, 2 Jie Lu, 1 , * and Kuncheng Li 1 , 5 , *
Acupuncture Modulates Resting State Hippocampal Functional Connectivity in Alzheimer Disease
Zhiqun Wang, 1 Peipeng Liang, 1 , 5 Zhilian Zhao, 1 Ying Han, 2 Haiqing Song, 2 Jianyang Xu, 3 Jie Lu, 1 , * and Kuncheng Li 1 , 4 , 5 , *
Observation on the efficacy of acupuncture and fire needle therapy for hand osteoarthritis
Different acupuncture and moxibustion methods at Heding (EX-LE 2) for knee osteoarthritis with yang-deficiency and cold-stagnation syndrome
Clinical study of fire acupuncture with centro-square needles for knee osteoarthritis
Wang B1, Hu J1, Zhang N1, Wang J1, Chen Z1, Wu Z1.
Traditional Chinese Medicine for Learning Disability among youth
Learning attitude and ability of the children are always a major concern for parents, some youth have more trouble in learning in comparison to others due to certain disability in their system, the following researches have demonstrated the effectiveness of TCM in assisting the youth regaining and recover from the issue.
Clinical efficacy on mental retardation in the children treated with JIN’s three scalp needling therapy and the training for cognitive and perceptual disturbance
Huang X, Yuan Q, Luo Q, Zeng H, Zheng X, Huang X, Yu Y, Wu Y.
Clinical research on children mental retardation treated with acupuncture
Huang JB1, Cao HF, Hu J, Liu LH, Wang Z, Lin H.
Acupuncture for promoting intelligence of children–an observation on 37 cases with mental retardation
Tian YP1, Qi R, Li XL, Wang YL, Zhang Y, Ji T, Hou CY, Wang LJ.
COVID-19
With the recent outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic, more and more people are skeptic in going out or get in contact with others.
Recent research has shown that TCM treatments and herbal formulas can help boost immunity and regulate the internal harmony for our body to fight against the virus, preventing infections, and with little or no side-effects.
There are also studies proven that TCM herbal formulas are also effective against flu-like illnesses, such as influenza.
TCM Herbal formula Yu Ping Feng San can regulate the immune system
Covid-19 has spread over the world and everyone fears becoming one of the confirmed cases on the list, however, it is already known that our immune system can fight the virus since thousands of infected have recovered from it, although the insight of how it happened is still uncertain.
The Traditional Chinese Herbal Formula “Yu Ping Feng San” has been widely used by TCM practitioners in regulating the immune system and has been clinically shown its promising results.
Yu Ping Feng San, an Ancient Chinese Herbal Decoction Containing Astragali Radix, Atractylodis Macrocephalae Rhizoma and Saposhnikoviae Radix, Regulates the Release of Cytokines in Murine Macrophages
Crystal Y. Q. Du, 1 , 2 Roy C. Y. Choi, 1 Ken Y. Z. Zheng, 2 Tina T. X. Dong, 1 David T. W. Lau, 1 and Karl W. K. Tsim 1 , *
Anti-inflammatory effect of Yu-Ping-Feng-San via TGF-β1 signaling suppression in rat model of COPD
Zhong-Shan Yang,1 Jin-Yuan Yan,2† Ni-Ping Han,1 Wei Zhou,1 Yu Cheng,1 Xiao-Mei Zhang,1 Ning Li,1 and Jia-Li Yuan1,*
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5080430/
The Effectiveness of Yin Qiao San against influenza
The symptoms and manifestation of Covid-19 and influenza are very similar, they both cause respiratory diseases, symptoms such as fever, cough, fatigue, body aches, etc. and sometimes it could lead to severe pneumonia.
Many believed that those who are vulnerable to influenza are also high-risk populations to Covid-19.
In TCM theory, the functions of Yin Qiao San are to “disperses wind-heat, clears heat, and relieves toxicity”, it is effective in upper respiratory tract infections.
During the outbreak of SARS-CoV in 2002, TCM herbal formulas have shown significant results in treating patients that are infected with the virus.
Traditional Chinese Medicine in the Treatment of Patients Infected with 2019-New Coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2): A Review and Perspective
Yang Yang*, Md Sahidul Islam*, Jin Wang, Yuan Li, Xin Chen
https://www.ijbs.com/v16p1708.htm
Effects of different principles of Traditional Chinese Medicine treatment on TLR7/NF-κB signaling pathway in influenza virus infected mice
Ying-Jie Fu, Yu-Qi Yan, Hong-Qiong Qin, Sha Wu, Shan-Shan Shi, Xiao Zheng, Peng-Cheng Wang, Xiao-Yin Chen, Xiao-Long Tang & Zhen-You Jiang
https://cmjournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13020-018-0199-4
In Vitro Fertilization
Statistics have shown that infertility is growing by the year, about 1 out of 4 couples will be affected by infertility disorder in the developing countries, many couples will turn to the option of in vitro fertilization and hoping to safely deliver a healthy baby.
However, a woman aged under 35 years old who undergoes IVF procedure only has a 39.6% success rate, while a woman aged over 40 years old will only have a success rate of 11.5%.
Studies has shown that acupuncture as an adjunctive treatment during IVF pregnancy could increase the success rate of delivering the baby, the treatments can promote and regulate blood flow to ovaries and uterus, reduce patient’s stress level and calm the patient, with minimal or no side-effects the patient can have a ready mind and body condition for the new comer.
Acupuncture and in vitro fertilisation research: current and future directions
Lee E Hullender Rubin , Belinda J Anderson , LaTasha B Craig
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29440044/
Management of Acupuncture as Adjuvant Therapy for In Vitro Fertilization
Wahyuningsih Djaali , Kemas Abdurrohim , Dwi Rachma Helianthi
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31871523/
The effects of acupuncture on pregnancy outcomes of in vitro fertilization: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Zheng-Yun Xie, Zhi-Hang Peng, Bing Yao , Li Chen , Yan-Yun Mu , Jie Cheng , Qian Li , Xi Luo , Peng-Yan Yang , You-Bing Xia