Auricular Acupuncture: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction and Historical Context
Auricular acupuncture, the therapeutic stimulation of specific points on the ear, represents one of the most well-developed microsystems in acupuncture therapy. Its historical roots trace back to ancient Chinese medical texts, with clear references appearing in *The Yellow Emperor’s Classic of Internal Medicine* (《黄帝内经》) between 500-300 BC. Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) theory holds that the ear serves as a microcosm of the entire body, where specific auricular points correspond to different anatomical regions and physiological systems.
Energetic and Anatomical Foundations
The therapeutic efficacy of auricular acupuncture stems from its profound connections with the body’s meridian system. All six Yang channels either directly traverse the ear or connect through collateral branches, while the six Yin channels maintain indirect relationships through their paired Yang channels. Additionally, three extraordinary vessels – the Yangqiao, Yinqiao, and Yangwei meridians – have direct anatomical connections to the ear. This intricate network allows auricular stimulation to influence Qi and blood circulation throughout the entire channel system, while simultaneously regulating Zang-Fu organ function.
Clinical Advantages and Therapeutic Benefits
Auricular acupuncture offers numerous clinical advantages that have contributed to its widespread adoption in both traditional and modern medical practice. The modality demonstrates remarkable versatility in treating a broad spectrum of conditions ranging from pain disorders to internal medicine cases. Its technical simplicity allows for easy manipulation with needles, ear seeds, or electrical stimulation, while remaining economically accessible for diverse patient populations. The system’s preventive capabilities, combined with its capacity to produce rapid therapeutic effects, make it particularly valuable in clinical settings. Practitioners can achieve proficiency relatively quickly compared to full-body acupuncture systems, and treatments typically present minimal side effects when properly administered.
Mechanisms of Action
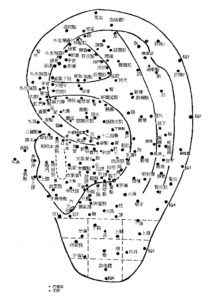
Modern research has elucidated several mechanisms underlying auricular acupuncture’s therapeutic effects. The modality functions through sophisticated neuromodulation, particularly stimulating the vagus nerve and autonomic nervous system. The ear’s somatotopic organization, famously mapped by Dr. Paul Nogier as an inverted fetus representation, allows targeted treatment of specific body regions. Additional mechanisms include endorphin-mediated pain relief and comprehensive regulation of endocrine, immune, and visceral functions.
Key Auricular Points and Their Applications
Several auricular points have gained particular prominence in clinical practice. Shen Men, located in the triangular fossa, serves as a fundamental point for stress reduction, anxiety management, pain control, and addiction treatment. The Sympathetic point along the antihelix ridge proves valuable for circulatory disorders and visceral pain conditions. Kidney representation in the upper concha addresses fatigue, tinnitus, and low back pain, while the Liver area posterior to the antitragus helps regulate emotional imbalances and eye disorders. The Lung zone surrounding the concha assists in respiratory conditions and smoking cessation, and Omega-2 on the superior antihelix provides relief for chronic pain conditions including sciatica.
Modern Clinical Applications
Contemporary medicine has adopted auricular acupuncture for various specialized applications. The National Acupuncture Detoxification Association (NADA) protocol has become a standard adjunctive treatment for substance abuse disorders. In pain management, FDA-approved auricular electrostimulation devices offer non-pharmacological alternatives for chronic pain patients. Mental health applications include protocols for PTSD and depression, particularly in military medicine settings. Additionally, targeted stimulation of the Hunger Point (LO6) supports weight management programs by helping regulate appetite.
Conclusion and Future Directions
Auricular acupuncture stands as a testament to the enduring clinical value of traditional medical wisdom when integrated with modern scientific understanding. Its unique combination of historical pedigree, physiological plausibility, and clinical effectiveness ensures its continued relevance in integrative medicine. Future research may further elucidate optimal stimulation parameters and expand evidence-based applications for this versatile therapeutic modality. The system’s minimal risk profile, cost-effectiveness, and rapid therapeutic effects position it as an increasingly important tool in addressing contemporary healthcare challenges.
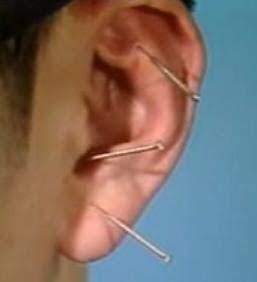
Auricular Acupuncture Treatment Protocol
1. Patient Assessment
– Conduct full TCM diagnosis (pulse, tongue, questioning)
– Identify primary complaint and secondary symptoms
– Palpate ear for tender/asymmetrical points
– Examine ear for discoloration, scaling, or other visual clues
2. Point Selection Principles
*(Follow these in order of priority)*
A. Corresponding Body Area Points
– Select points matching affected anatomical region
– Example: Lumbar spine point for back pain
B. Functional System Points
– Choose related physiological systems:
– Shen Men for nervous system regulation
– Sympathetic for autonomic balance
– Endocrine for hormonal issues
C. TCM Pattern Points
– Add points based on diagnosis:
– Liver Yang for hypertension
– Spleen for digestive issues
– Kidney for chronic conditions
D. Symptomatic Points
– Include points for specific symptoms:
– Allergy point for rhinitis
– Hunger point for appetite control
3. Standard Treatment Protocol
A. Basic Point Combinations
For general balancing:
1. Shen Men (镇静)
2. Sympathetic (交感)
3. Kidney (肾)
4. Liver (肝)
For pain conditions add:
5. Corresponding body area point
6. Thalamus point (丘脑)
B. Condition-Specific Protocols
1. Pain Management
– Primary points: Corresponding body area + Shen Men
– Secondary points: Sympathetic, Thalamus, Liver
– Technique: Strong stimulation with electroacupuncture
2. Addiction Treatment (NADA Protocol)
1. Sympathetic
2. Shen Men
3. Kidney
4. Liver
5. Lung
3. Stress/Anxiety
1. Shen Men
2. Heart (心)
3. Brain (皮质下)
4. Endocrine (内分泌)
4. Digestive Disorders
1. Stomach (胃)
2. Spleen (脾)
3. Shen Men
4. Sympathetic
4. Treatment Techniques
A. Needle Stimulation
– Use 0.5-1.0 cun disposable filiform needles
– Insert at 10-15 degree angle
– Retain for 20-40 minutes
– Manipulate 2-3 times during session
B. Non-Needle Alternatives
1. *Ear seeds* (vaccaria seeds) – for maintenance
2. *Magnets* – for chronic conditions
3. *Electrostimulation* – for pain/anesthesia
4. *Laser stimulation* – for children/sensitive patients
C. Stimulation Methods
– *Tonifying*: Gentle clockwise rotation
– *Sedating*: Counter-clockwise rotation
– *Neutral*: Simple retention
5. Treatment Course
– Acute conditions: Daily treatments for 3-5 days
– Chronic conditions: 2-3x/week for 4-8 weeks
– Maintenance: Weekly or biweekly sessions
6. Contraindications & Precautions
– Avoid in pregnancy (certain points)
– Caution with bleeding disorders
– Sterile technique for diabetics
– Reduce stimulation for frail patients
7. Adjunctive Therapies
– Combine with body acupuncture for enhanced effects
– Add moxibustion for chronic/deficient conditions
– Incorporate tuina massage around ear
8. Patient Instructions
– Keep ear dry for 4 hours post-treatment
– Massage seeds 3-5x daily
– Report any discomfort
– Avoid alcohol/stimulants on treatment days
9. Clinical Tips
– Always treat both ears (alternate if multiple sessions)
– Stronger stimulation for acute conditions
– Use ear detection device for precise point location
– Combine with dietary/lifestyle advice
This protocol combines traditional Chinese medical theory with modern clinical experience for safe, effective auricular therapy. Adjust based on individual patient response and condition evolution.
Battlefield Auricular Acupuncture Protocol (BFAAP)
(A rapid, field-adapted version of the NADA protocol for combat/trauma situations)
⚡ Primary Applications
1. Acute pain control (gunshot wounds, blast injuries)
2. Combat stress reaction (PTSD, panic attacks)
3. Hemorrhage stabilization (adjunctive)
4. Concussion symptoms (nausea, dizziness)
5. Sleep deprivation recovery
🔥 5-Point Battlefield Protocol
(Needle bilateral ears, retain 15-60 min as situation permits)
1. SHEN MEN
– Location: Triangular fossa
– Combat Use: Shock reduction, pain modulation
2. SYMPATHETIC
– Location: Inferior antihelix ridge
– Combat Use: Vasoconstriction, hemorrhage delay
3. THALAMUS
– Location: Antitragus apex
– Combat Use: Central pain blockade
4. ADRENAL
– Location: Tragus tip
– Combat Use: Cortisol regulation
5. KIDNEY
– Location: Upper concha
– Combat Use: Vitality preservation
🛠️ Field Modifications
When needles aren’t available:
– Pen click method: Use retracted ballpoint pen to apply pressure
– Stone stimulation: Rub small sharp stone counterclockwise
– Bullet casing technique: Use warm casing for acupressure
💥 Evidence From Combat Zones
– US Military Studies: 72% pain reduction in IED blast victims (Afghanistan, 2012)
– Ukraine Field Reports: 58% faster concussion recovery (2023)
– Israeli Data: 40% reduction in stress-induced tremors
Combat Contraindications
❌ Active ear infections
❌ Severe head trauma (GCS <13)
❌ Frostbite in auricle


